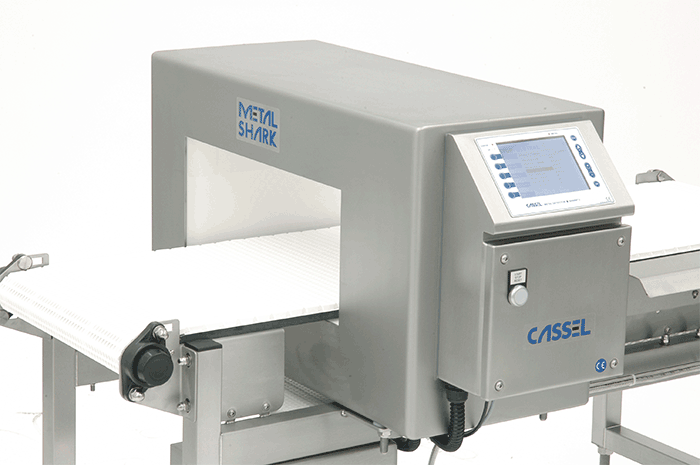
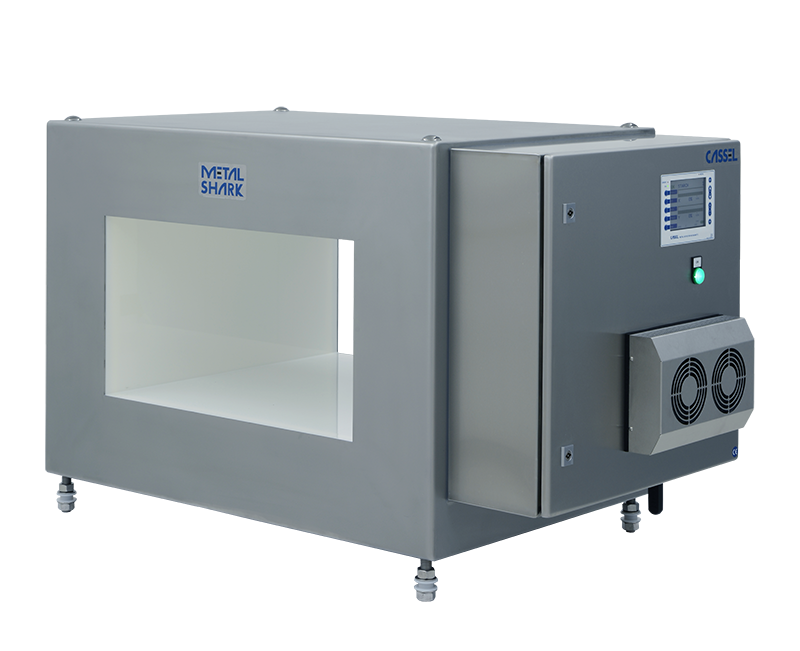
How do metal detection systems work?
An industrial metal detector senses disturbances in a balanced electromagnetic field, indicating the presence of metal contamination. A digital signal processor analyzes the signals to detect the contaminant but must ignore the product. Superior systems use special filtering to boost the contaminant signal for better sensitivity.
What is detectable by metal detection technology?
Metal detection equipment will detect ferrous and non-ferrous metals only. To be detectable, metals need to be conductive, magnetic, or both.
- Ferrous – These metals contain iron. Ferrous metals have both magnetic and conductive properties. They are easy to detect.
- Non-ferrous – Examples include aluminum, copper, tin, lead, brass, and silver. Nonferrous metals are conductive but non-magnetic. They are slightly more difficult to detect.
What is multiphase technology and how does it handle product effect?
Product effect occurs in metal detection systems because most food items are conductive or magnetic. For example, iron-rich food such as fortified cereals or red meat will mimic the presence of metal contamination and cause the signal to become unbalanced. In addition, moist or salty foods such as deli meats or salty crackers are conductive and can have a similar effect. Multiphase technology offers a superior method for handling product effect. Continuous adjustment to the temperature and orientation of the product changes the phase angle for improved sensitivity. And the existence of a contaminant is not determined until the product has passed fully through the aperture.
What is the longevity of a metal detector?
An industrial metal detector, on average, can last up to 20 years and sometimes even longer. CASSEL Inspection works with every customer through the life of their system to support service needs and to ensure optimal performance.
How do you test an industrial metal detector?
Frequent testing must be performed on all metal detection equipment. For valid sensitivity rating, the standard protocol is to use a metal sphere embedded in plastic, running from 0.3mm to 10mm in diameter. The sphere must pass through the center of the aperture, where the weakest signal is. Metal spheres are used because of their consistent shape, which means there is no orientation effect. Ferrous, non-ferrous, and type 316 stainless steel should all be tested, one after the other.
CASSEL metal detector equipment is inspected annually (at a minimum) by a neutral third party to ensure that industry standards are met.
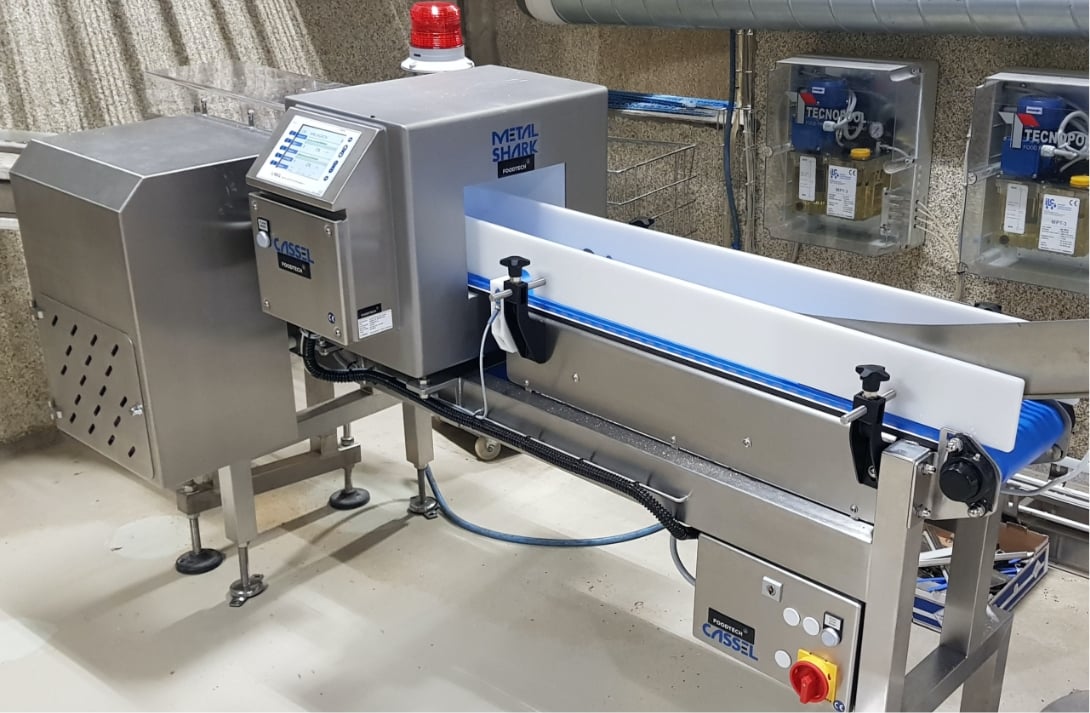
What are the different applications for an industrial metal detector?
Metal detection technology can be useful for inspecting a vast range of products. It is commonly used to assess the safety of packaged products. For example, any product in the grocery store might be inspected using metal detection equipment, typically after packaging. Unpackaged bulk flow products can also be inspected during processing, as well as pipeline products such as soups, slurries, or dairy products. Other important applications for metal detection systems include pharmaceuticals, recycled goods, and non-woven materials.
What kinds of contaminants are detectable in a typical metal detector?
How small of a metal contaminant can be detected in a metal detector?
Is metal detection or X-ray inspection better for my application?
What’s the best sensitivity I can get on my X-ray system?
Are CASSEL inspection detection systems customizable?